Economic
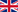
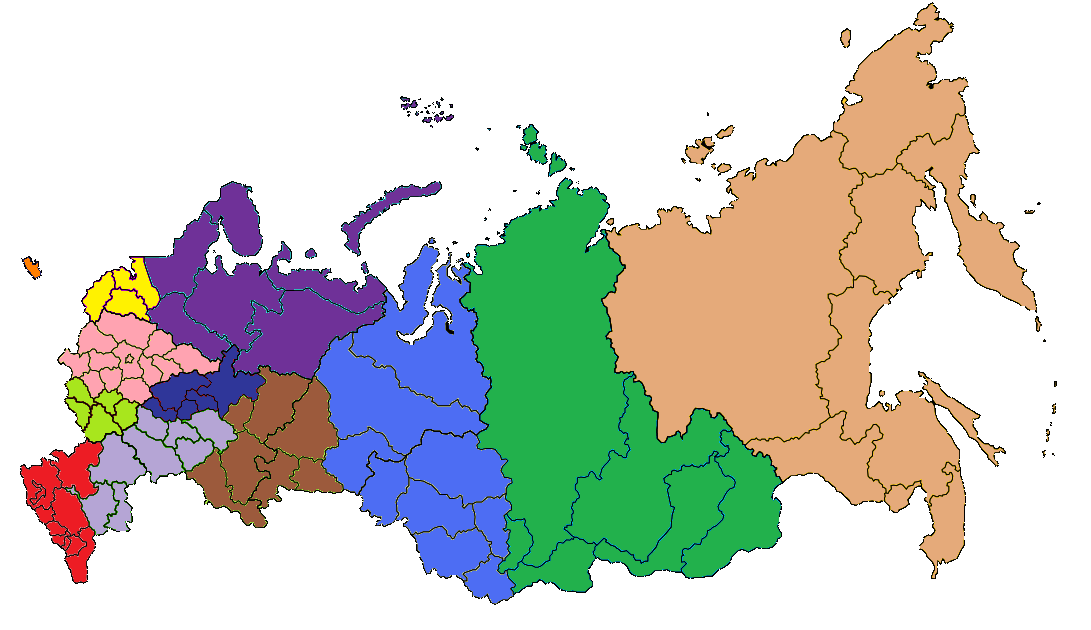 The territory of Russia is devided into eleven economic regions: Severo-Zapadny (North-West), Severny (North), Tcentralny (Center), Volgo-Vyatsky (Volga-Vyatka), Tcentralno-Chernozemniy (Center-Chernozemic) , Povolzhsky (Volga), Severo-Kavkazsky (North-Caucasus) Uralsky (Ural), Zapadno-Sibirsky (West-Siberia), Vostochno-Sibirsky (East-Siberia), Dalnevostochny (Far-East) plus Kaliningrad which has a status of a Special Economic Zone.
The territory of Russia is devided into eleven economic regions: Severo-Zapadny (North-West), Severny (North), Tcentralny (Center), Volgo-Vyatsky (Volga-Vyatka), Tcentralno-Chernozemniy (Center-Chernozemic) , Povolzhsky (Volga), Severo-Kavkazsky (North-Caucasus) Uralsky (Ural), Zapadno-Sibirsky (West-Siberia), Vostochno-Sibirsky (East-Siberia), Dalnevostochny (Far-East) plus Kaliningrad which has a status of a Special Economic Zone.
The economy of the Russian Federation is export oriented with positive trade balance (USD 150 bln). In 2015 export reached USD 346 bln (-30%) and import USD 197 bln (-42%). The reason for sharp decrease of export and import were low prices for oil and growing exchange rate of RUB/USD considering that main export income is from natural resources including oil and gas.
Despite recent economic reforms and initiated long term modernization programs in different sectors, the Russian economy remains to be very oil and gas dependent and sensitive to international energy resources’ price changes.
Russian GDP reached USD 3 398 bln in 2015 (-3,9%) and the economy was in a slight recession. The forecast GDP in 2016-2017 is unclear and depends on oil prices and geopolitical situation. European comission expects the decrease of GDP for 0.5% in 2016 following by increase for 1.0% in 2017.
|
|
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
|
GDP growth Industrial Production growth Oil price USD Interest rate (Central Bank of RF, refunding) |
1.3% 0.3% 97 8.25% |
0.6% 3.9% 86 8.25% |
-3.9% -3.7% 38 (December) 8.25% (11% from 01.01.2016) |
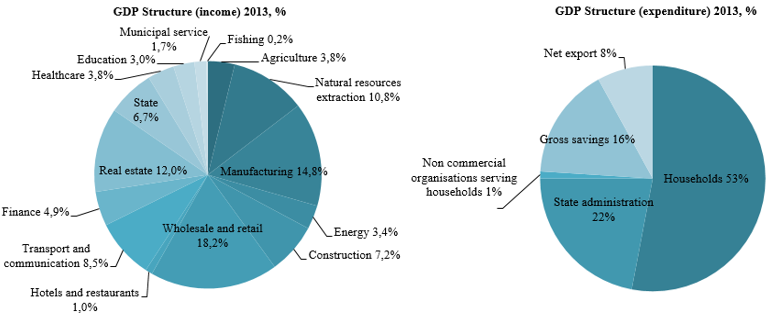
Structure of the Russia GDP (by type of economic activity) reflects its main sources such as trade, manufacturing, real estate operations and extraction of natural resources.
Sources: Ministry of Economic Development, Ministry of Finance, Federal State Statistics Service