Macro
 Russia is the world's largest country in terms of territory; it takes number six in terms of GDP (PPP) and number nine in terms of population.
Russia is the world's largest country in terms of territory; it takes number six in terms of GDP (PPP) and number nine in terms of population.
Considering a consumer market of over 146 million people, vast natural resources, highly educated workforce and recent government initiatives Russia has a very high growth potential.
After the crisis of 2009 the Russian economy has recovered rather fast even though GDP growth rate has decreased. High oil prices and growing investments from both state and private sources stimulated the Russian economy. However, in 2015 low oil prices and economic sanctions leaded to the slight recession in Russian Federation.
Main macroeconomic indicators (2015)
|
Area Population GDP total, PPP GDP per capita GDP growth Inflation Unemployment rate Life expectancy |
17 125 407 sq km 146.3 million USD 3 398 bln USD 23 434 - 3.7% 12,8% 5.4% 65.1 years (male), 76.3 years (female) |
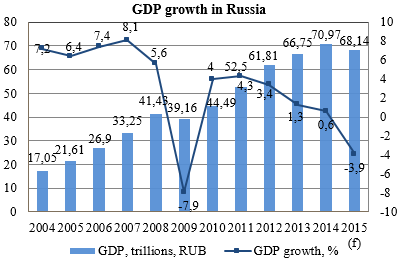
According to the Federal State Statistics Service of Russian Federation the economic growth was 0.6% in 2014 compared with 1.3% in 2013. The Russian government expects the decreasing of GDP for 3.9% in 2015. The World Bank and S&P prognoses for Russian GDP are approximatly the same.
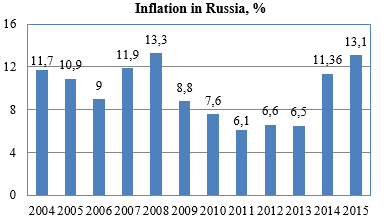
The inflation level was stable in 2011-2013 (between 6.1 and 6.5%) But in 2015 the level of inflation is expected to rise up to 12%. The main reasons for inflation growth are: low oil prices, embargo on an import of a number of food categories, growth of tariffs for energy and other commodities, increase of taxes and recession in production.
The Russian budget for 2015-2017 was made assuming the oil price 80 USD for barrel. However the price for oil in December 2015 dropped down to 37 USD for barrel (Brent). The budget of 2016 is planed now assuming price for oil of 50 USD. At the same time the Central Bank of Russian Federation is preparing the "shock" scenario for the economy in a case the prise for oil drops down to 35 USD for barrel.
Sources: Ministry of Finance, EBRD, IMF, Federal State Statistics Service